MAX9724A 查看數據表(PDF) - Maxim Integrated
零件编号
产品描述 (功能)
生产厂家
MAX9724A
MAX9724A Datasheet PDF : 19 Pages
| |||
60mW, DirectDrive, Stereo Headphone Amplifier
with Low RF Susceptibility and Shutdown
Detailed Description
The MAX9724A/MAX9724B stereo headphone ampli-
fiers feature Maxim’s patented DirectDrive architecture,
eliminating the large output-coupling capacitors
required by conventional single-supply headphone
amplifiers. The device consists of two 60mW Class AB
headphone amplifiers, undervoltage lockout
(UVLO)/shutdown control, charge pump, and compre-
hensive click-and-pop suppression circuitry (see the
Functional Diagram/Typical Operating Circuits). The
charge pump inverts the positive supply (VDD), creat-
ing a negative supply (PVSS). The headphone ampli-
fiers operate from these bipolar supplies with their
outputs biased about PGND (Figure 1). The benefit of
this PGND bias is that the amplifier outputs do not have
a DC component. The large DC-blocking capacitors
required with conventional headphone amplifiers are
unnecessary, conserving board space, reducing sys-
tem cost, and improving frequency response. The
MAX9724A/MAX9724B feature an undervoltage lockout
that prevents operation from an insufficient power sup-
ply and click-and-pop suppression that eliminates audi-
ble transients on startup and shutdown. The
MAX9724A/MAX9724B also feature thermal-overload
and short-circuit protection.
DirectDrive
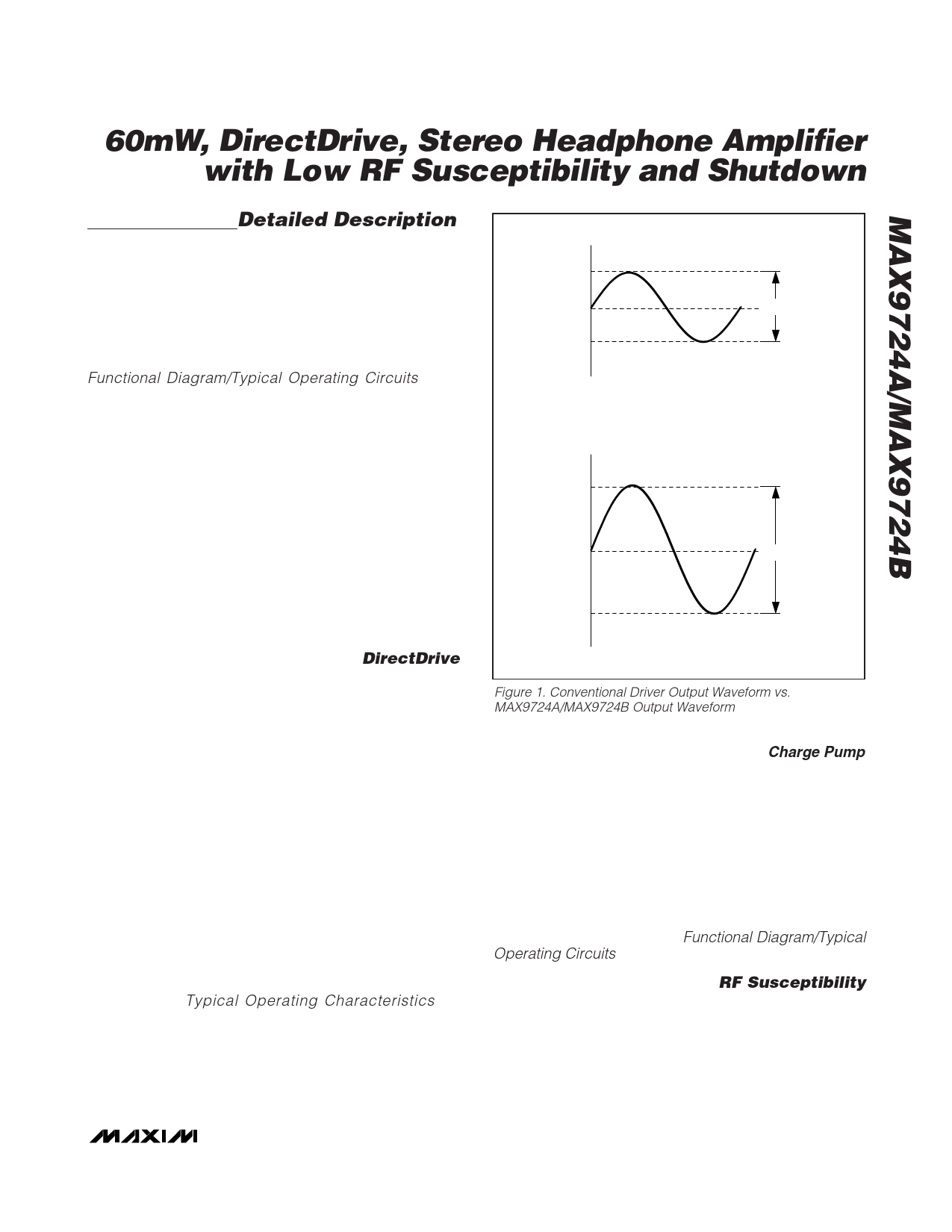
Conventional single-supply headphone amplifiers have
their outputs biased about a nominal DC voltage (typi-
cally half the supply) for maximum dynamic range.
Large-coupling capacitors are needed to block this DC
bias from the headphone. Without these capacitors, a
significant amount of DC current flows to the head-
phone, resulting in unnecessary power dissipation and
possible damage to both headphone and headphone
amplifier.
Maxim’s patented DirectDrive architecture uses a
charge pump to create an internal negative supply volt-
age, allowing the MAX9724A/MAX9724B outputs to be
biased about GND. With no DC component, there is no
need for the large DC-blocking capacitors. The
MAX9724A/MAX9724B charge pumps require two
small ceramic capacitors, conserving board space,
reducing cost, and improving the frequency response
of the headphone amplifier. See the Output Power vs.
Load Resistance and Charge-Pump Capacitor Size
graph in the Typical Operating Characteristics for
details of the possible capacitor sizes. There is a low
DC voltage on the amplifier outputs due to amplifier off-
set. However, the offsets of the MAX9724A/MAX9724B
are typically 1.5mV, which, when combined with a 32Ω
load, results in less than 47µA of DC current flow to the
headphones.
VOUT
VDD
VDD/2
VDD
GND
CONVENTIONAL DRIVER-BIASING SCHEME
VOUT
VDD
GND
2VDD
-VDD
DirectDrive BIASING SCHEME
Figure 1. Conventional Driver Output Waveform vs.
MAX9724A/MAX9724B Output Waveform
Charge Pump
The MAX9724A/MAX9724B feature a low-noise charge
pump. The 270kHz switching frequency is well beyond
the audio range and does not interfere with audio sig-
nals. The switch drivers feature a controlled switching
speed that minimizes noise generated by turn-on and
turn-off transients. The di/dt noise caused by the para-
sitic bond wire and trace inductance is minimized by
limiting the switching speed of the charge pump.
Although not typically required, additional high-fre-
quency noise attenuation can be achieved by increas-
ing the value of C2 (see the Functional Diagram/Typical
Operating Circuits).
RF Susceptibility
Modern audio systems are often subject to RF radiation
from sources like wireless networks and cellular phone
networks. Although the RF radiation is out of the audio
band, many signals, in particular GSM signals, contain
bursts or modulation at audible frequencies. Most ana-
log amplifiers demodulate the low-frequency envelope,
adding noise to the audio signal. The architecture of
_______________________________________________________________________________________ 9