NX25F011A 查看數據表(PDF) - NexFlash -> Winbond Electronics
零件编号
产品描述 (功能)
生产厂家
NX25F011A
NX25F011A Datasheet PDF : 26 Pages
| |||
NX25F011A
NX25F041A
The factory default setting for bits CF8-CF0 is: 0 0000 1001
B(write protect range = none, read uses falling edge of the
clock, and pin 1 = no connect). Bits CF15-CF9 are
reserved. When writing to the configuration register
CF15-CF9 should be 0. When reading, the settings of
CF15-CF9 should be ignored.
Standard write endurance rating of the memory array
allows for 10,000 erase/write cycles. Extended endurance
to 100,000 cycles is possible using ECC techniques like
those provided in the Serial Flash Development Kit.
The rating of the configuration register EEPROM cells is
1,000 write cycles. This is more than adequate considering
the configuration seldom needs to be changed. To mini-
mize writes to the configuration register, the configuration
register should be read upon power-up to determine if a
change is required. If no change is needed, the write
configuration command can be skipped. This process will
extend the life of the configuration register and save
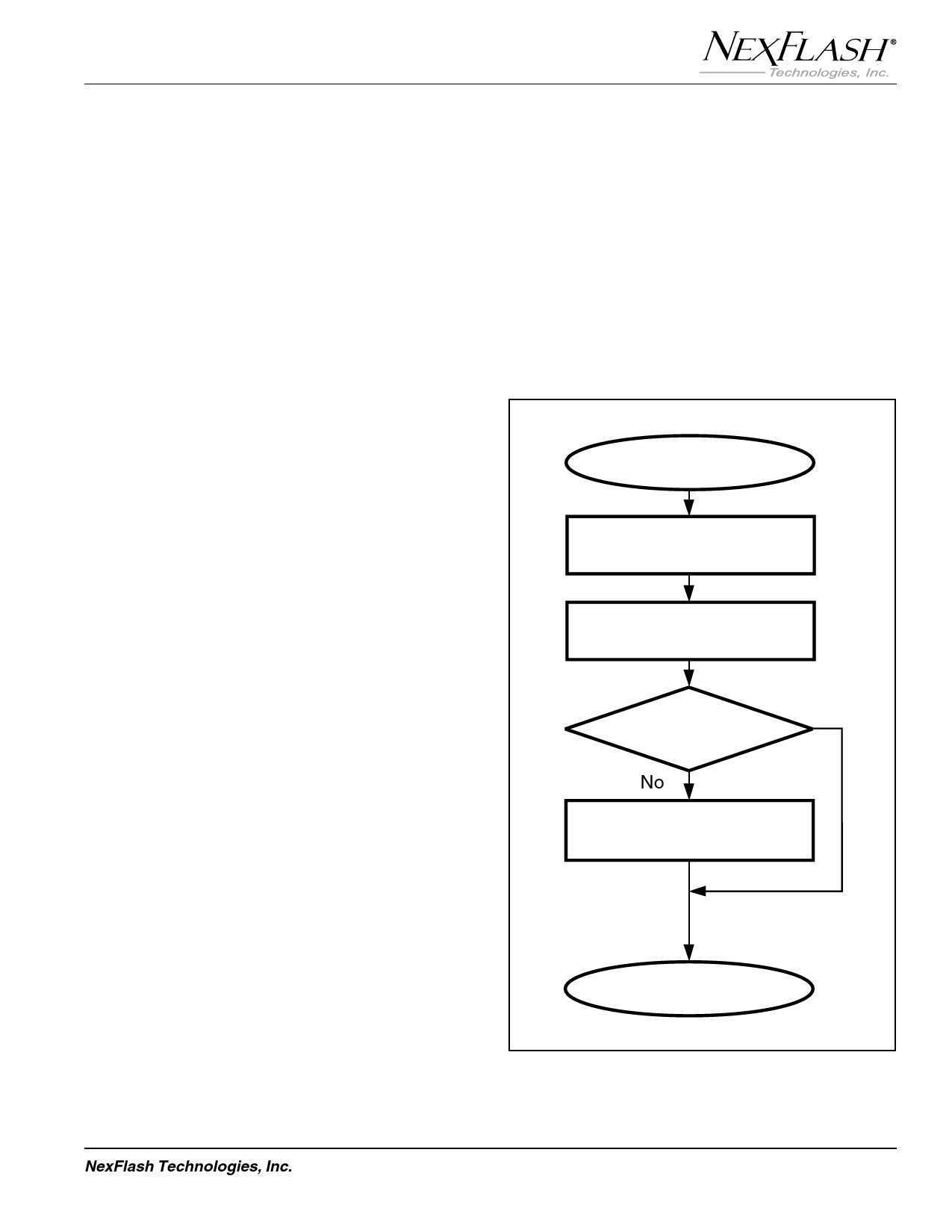
processing time (Figure 7).
Alternate Oscillator Frequency, AF
Flash memory devices have charge pump oscillators to
generate internal high-voltages used for programming
non-volatile memory cells. In some applications, the oscil-
lator frequency of the charge pump may cause noise
interference. To solve this problem, an alternate oscillator
frequency (AF) can be selected by setting bit CF[8] of the
configuration register. The alternate frequency is a
non-harmonic frequency of the standard oscillator. The
factory default setting is for the standard oscillator
frequency, AF equal to 0.
AF=0 Standard Oscillator Frequency is used.
AF=1 Alternate Oscillator Frequency is used.
Write Protect Range and Direction, WR[3:0], WD
The write protect range and direction bits WR[3:0] and WD
are located at configuration bits CF[7:4] and CF[3] respec-
tively. The write protect range and direction bits select how
the array is protected. They work in conjunction with the
WP input pin, valid only if WP is inactive (high). WR[3:0] can
select write protection of all sectors, none of the sectors, or
specific sectors grouped in blocks of 32 (~8 KB). The WD
bit specifies whether the protected block range starts from
the first sector, address 0 (000H), or from the last sector
(1FFH for the NX25F011A and 7FF for the NX25F041A).
Table 2 lists the write protect sector range for both devices.
Once protected, all further writes to sectors within the
range will be ignored. The factory default setting is with no
write protected sectors, WR=[0,0,0,0] and WD=1.
Read Clock Edge, RCE
The Read Clock Edge bit (RCE) is located at configuration
bit location CF[2]. It selects which edge of the clock (SCK)
1 is used while reading data out of the device. Although the
SPI protocol specifies that data is written during the rising
edge and read on the falling edge of the clock, the output
can be driven on the rising edge of the clock by setting the
2 configuration registers RCE bit to a 1. Using the rising edge
of clock for data reads may be beneficial to the timing of
some high-speed systems. The factory default setting is for
reading on the falling edge of SCK.
3 RCE=0 Read data is output on the falling edge of SCK.
RCE=1 Read data is output on the rising edge of SCK.
4
System Power-up
5
Read Device Information Sector,
Verify Device Density and Type
6
Read Configuration Register
Verify bits are Set as Needed
7
Configuration
Yes
Setting is Correct?
8
No
Write Configuration Register
9
to Correct Setting
10
11
Application Routines
12
Figure 7. Flow Chart for Checking the Configuration
Register upon Power-up
NexFlash Technologies, Inc.
7
PRELIMINARY NXSF014B-0699
06/11/99