AD627(RevA) 查看數據表(PDF) - Analog Devices
零件编号
产品描述 (功能)
生产厂家
AD627
(Rev.:RevA)
(Rev.:RevA)
AD627 Datasheet PDF : 16 Pages
| |||
AD627
VCM
VDIFF
2
V+
+IN
VDIFF
2
–IN
V–
REF
100k⍀
+VS
–IN 2k⍀
–VS
EXTERNAL GAIN RESISTOR
25k⍀ RG 25k⍀
Q1
Q2
A1
100k⍀
+VS
2k⍀ +IN
–VS
A2
OUTPUT
200k⍀
VA
200k⍀
–VS
Figure 34. Amplifying Differential Signals with a Common-Mode Component
Table I. Recommended Values of Gain Resistors
Desired
Gain
5
6
7
8
9
10
15
20
25
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
200
500
1000
1% Std Table
Value of RG, ⍀
∞
200 k
100 k
68.1 k
51.1 k
40.2 k
20 k
13.7 k
10 k
8.06 k
5.76 k
4.53 k
3.65 k
3.09 k
2.67 k
2.37 k
2.1 k
1.05 k
412
205
Resulting
Gain
5
6
7
7.93
8.91
9.98
15
19.6
25
29.81
39.72
49.15
59.79
69.73
79.9
89.39
99.24
195.48
489.44
980.61
Reference Terminal
The reference terminal potential defines the zero output voltage
and is especially useful when the load does not share a precise
ground with the rest of the system. It provides a direct means of
injecting a precise offset to the output. The reference terminal is
also useful when bipolar signals are being amplified as it can be
used to provide a virtual ground voltage.
Since the AD627 output voltage is developed with respect to the
potential on the reference terminal, it can solve many grounding
problems by simply tying the REF pin to the appropriate “local
ground.” The REF pin should however be tied to a low imped-
ance point for optimal CMR.
Input Range Limitations in Single Supply Applications
In general, the maximum achievable gain is determined by the
available output signal range. However, in single supply applica-
tions where the input common mode voltage is close to or equal
to zero, some limitations on the gain can be set. While the In-
put, Output and Reference Pins have ranges that are nominally
defined on the specification pages, there is a mutual interdepen-
dence between the voltage ranges on these pins. Figure 34 shows
the simplified schematic of the AD627, driven by a differential
voltage VDIFF which has a common mode component, VCM. The
voltage on the output of op amp A1 is a function of VDIFF, VCM,
the voltage on the REF pin and the programmed gain. This
voltage is given by the equation:
VA1 = 1.25 (VCM + 0.5 V) – 0.25 VREF – VDIFF (25 kΩ/RG – 0.625)
We can also express the voltage on A1 as a function of the ac-
tual voltages on the –IN and +IN pins (V– and V+)
VA1 = 1.25 (V– + 0.5 V) – 0.25 VREF – (V+ – V–) 25 kΩ/RG
A1’s output is capable of swinging to within 50 mV of the nega-
tive rail and to within 200 mV of the positive rail. From either of
the above equations, it is clear that an increasing VREF, (while it
acts as a positive offset at the output of the AD627), tends to
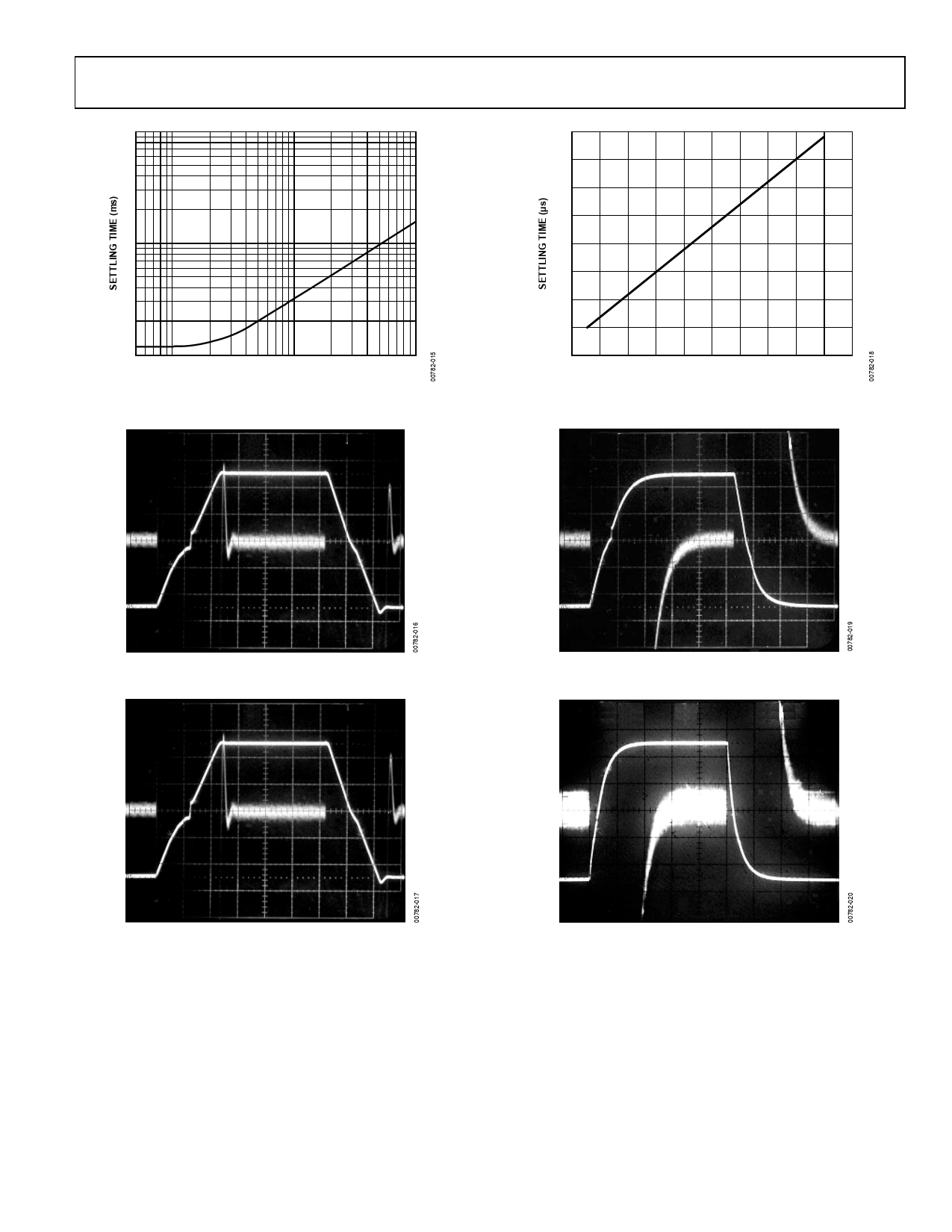
decrease the voltage on A1. Figures 35 and 36 show the maxi-
mum voltages that can be applied to the REF pin, for a gain of
five for both the single and dual supply cases. Raising the input
common-mode voltage will increase the voltage on the output of
A1. However, in single supply applications where the common-
mode voltage is low, a differential input voltage or a voltage on
REF that is too high can drive the output of A1 into the ground
rail. Some low side headroom is added by virtue of both inputs
being shifted upwards by about 0.5 V (i.e., by the VBE of Q1
and Q2). The above equations can be used to check that the
voltage on amplifier A1 is within its operating range.
Table II gives values for the maximum gains for various single
supply input conditions. The resulting output swings shown
refer to 0 V. The voltages on the REF pins has been set to either
Table II. Maximum Gain for Low Common-Mode Single Supply Applications
VIN
± 100 mV, VCM = 0 V
± 50 mV, VCM = 0 V
± 10 mV, VCM = 0 V
V– = 0 V, V+ = 0 V to 1 V
V– = 0 V, V+ = 0 mV to 100 mV
V– = 0 V, V+ = 0 mV to 10 mV
REF
Pin
2V
2V
2V
1V
1V
1V
Supply
Voltage
+5 V to +15 V
+5 V to +15 V
+5 V to +15 V
+10 V to +15 V
+5 V to +15 V
+5 V to +15 V
RG (1%
Tolerance)
28.7 kΩ
10.7 kΩ
1.74 kΩ
78.7 kΩ
7.87 kΩ
7.87 Ω
Resulting
Max Gain
12.0
23.7
119.9
7.5
31
259.1
Output Swing
WRT 0 V
0.8 V to 3.2 V
0.8 V to 3.2 V
0.8 V to 3.2 V
1 V to 8.5 V
1 V to 4.1 V
1 V to 3.6 V
REV. A
–11–